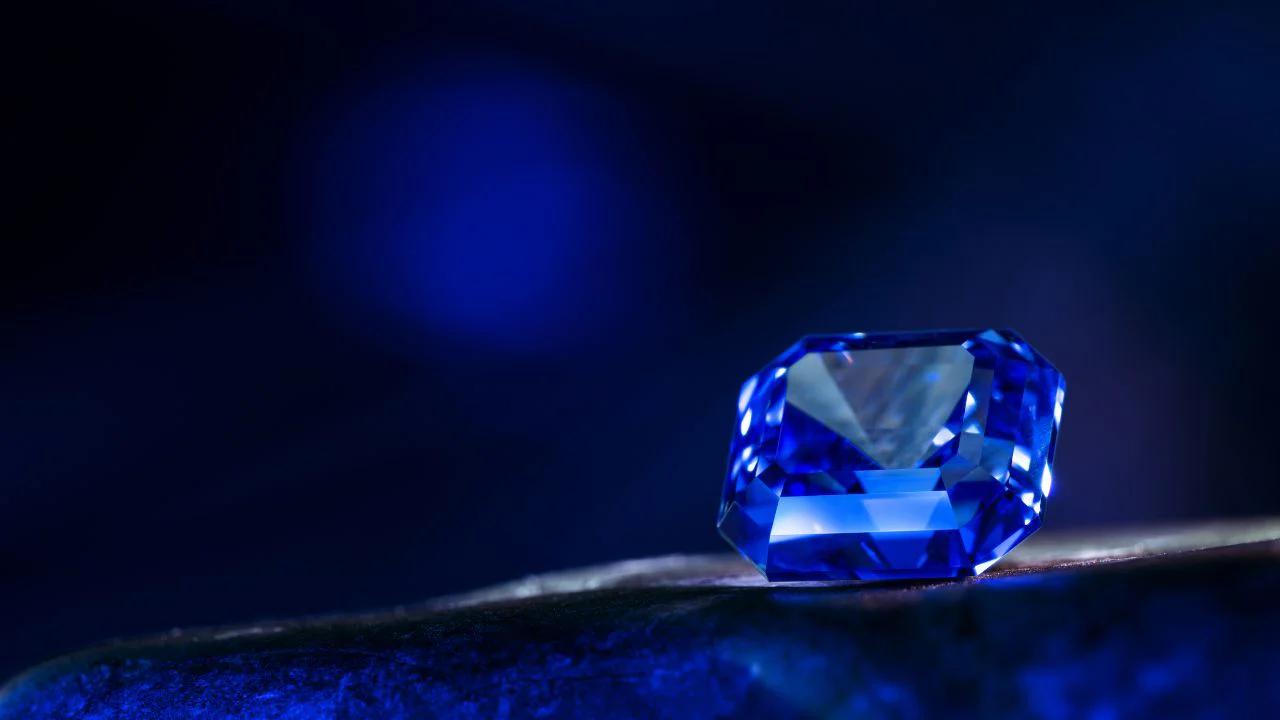
Blue sapphire, one of the most treasured gemstones in the world, is known for its mesmerizing deep blue hue and remarkable hardness. For centuries, this gemstone has symbolized royalty, wisdom, and divine favor. Its journey from the depths of the earth to a polished gem adorning fine jewelry is a fascinating tale of nature, craftsmanship, and commerce. Understanding this journey offers insights into the value, rarity, and significance of every blue sapphire.
The Formation of Blue Sapphire in Nature
Blue sapphire is a variety of the mineral corundum, composed primarily of aluminum oxide. The presence of trace elements like iron and titanium gives the stone its rich blue color. These gemstones form deep within the earth’s crust under intense pressure and high temperatures. Over millions of years, tectonic activities and geological processes push these stones closer to the surface.
Blue sapphires are typically found in alluvial deposits, where water has eroded surrounding rocks and concentrated the gemstones in riverbeds. Primary deposits also exist, where the stones are still embedded in their host rock. Major sources of blue sapphire include Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Madagascar, Thailand, Australia, and Montana in the United States.
Mining the Precious Gem
The journey of a blue sapphire begins in mines, which are often located in remote areas with challenging environments. There are two primary types of mining used to extract sapphires: alluvial mining and hard rock mining.
Alluvial mining is the most traditional method. Miners sift through gravel and soil in riverbeds, washing the material to separate the gemstones. This method is labor-intensive but less damaging to the environment compared to hard rock mining.
Hard rock mining, on the other hand, involves digging into the earth to extract sapphire-bearing rocks. This technique is more invasive and requires heavy machinery, but it is often necessary when sapphires are found deep underground.
After mining, the raw sapphires are sorted by size, color, and quality. Most rough stones are far from the sparkling blue gems seen in jewelry stores and need significant processing to reveal their true beauty.
Sorting and Grading the Rough Sapphires
Once extracted, the rough Blue sapphire undergo a detailed sorting and grading process. This stage is crucial in determining the future of each stone. Expert gemologists analyze the size, color saturation, clarity, and crystal structure of each rough gem.
Color is the most important factor in determining the value of a blue sapphire. The most prized sapphires display a deep, velvety blue hue with strong saturation and minimal zoning. Clarity is also critical—although minor inclusions are acceptable, eye-clean sapphires are more valuable.
In addition to natural factors, the origin of the stone can influence its value. Sapphires from Kashmir, for instance, are extremely rare and fetch premium prices due to their history and quality.
Cutting and Polishing: Revealing the Inner Beauty
The cutting process is where the rough stone begins to transform into a polished gem. Skilled lapidaries, or gemstone cutters, study each rough blue sapphire to determine the best way to cut it for maximum brilliance and minimal waste. This task requires immense precision, as a single mistake can ruin a valuable stone.
The cut must take into account the stone’s color zoning, inclusions, and overall shape. The goal is to enhance the stone’s color while maximizing its size and clarity. Once the appropriate cut is selected—whether oval, cushion, round, or emerald—the sapphire is carefully faceted to reflect light beautifully.
Polishing follows cutting, giving the stone its final luster. The result is a stunning blue sapphire that reflects the culmination of nature’s artistry and human skill.
Heat Treatment and Enhancement
Many blue sapphires undergo heat treatment to improve their color and clarity. This process involves heating the gemstone to high temperatures in a controlled environment. Heat treatment is a common and accepted practice in the gemstone industry, and it can enhance the stone’s appearance without introducing foreign substances.
It’s important to note that not all sapphires are treated. Untreated stones with exceptional color and clarity are exceedingly rare and highly valuable. Ethical sellers always disclose any treatments performed on a blue sapphire.
Certification and Authentication
Before reaching the market, a blue sapphire often undergoes certification from a recognized gemological laboratory. Labs like GIA (Gemological Institute of America) and AGL (American Gemological Laboratories) examine the stone to verify its authenticity, origin, and any treatments applied.
Certification provides confidence to buyers and sellers, ensuring transparency and protecting the stone’s value. It also includes detailed information about the gemstone’s dimensions, weight, and color grading.
From Dealer to Retail: Entering the Market
Once certified, blue sapphires enter the gemstone market, passing through a network of dealers, wholesalers, and jewelers. Dealers purchase rough or cut stones directly from mining regions or through auctions and trade shows. They then sell these gems to wholesalers or designers who incorporate them into fine jewelry.
At the retail level, the final product may appear as a solitaire ring, a pendant, earrings, or part of a larger jewelry piece. Each blue sapphire carries a story of its origin, craftsmanship, and journey—a story that adds emotional and material value to the gem.
Ethical Sourcing and the Modern Market
In recent years, there has been growing awareness around ethical sourcing in the gemstone industry. Consumers want assurance that their Blue sapphire was mined and processed without exploiting workers or harming the environment. As a result, many jewelers now emphasize conflict-free sourcing and work with mines that adhere to fair labor practices and environmental standards.
Blockchain technology and traceability tools are also helping to provide greater transparency in the supply chain. Buyers can now learn where and how their blue sapphire was sourced, adding a layer of trust and accountability to the purchase.
The Enduring Allure of Blue Sapphire
From ancient times to the modern age, blue sapphire has captured hearts and imaginations. Its journey from mine to market is a blend of natural wonder and human ingenuity. Each step—mining, sorting, cutting, treating, certifying, and selling—plays a vital role in bringing the stone to life.